Optical illusions convex figures. Visual illusions
Illusion is an optical illusion.
Types of optical illusion:
optical illusion based on color perception;
optical illusion based on contrast;
twisting illusions;
optical illusion of depth perception;
optical illusion of size perception;
contour optical illusion;
optical illusion "shifters";
Ames room;
moving optical illusions.
stereo illusions, or, as they are also called: “3d pictures”, stereo images.
ILLUSION OF BALL SIZE
Isn't it true that the size of these two balls is different? Is the top ball larger than the bottom?
In fact, this is an optical illusion: these two balls are absolutely equal. You can use a ruler to check. By creating the effect of a receding corridor, the artist managed to deceive our vision: the top ball seems larger to us, because our consciousness perceives it as a more distant object.
ILLUSION OF A. EINSTEIN AND M. MONROE
If you look at the picture from close distance, you see the brilliant physicist A. Einstein.

Now try to move a few meters away, and... miracle, in the picture there is M. Monroe. Here everything seems to have gone without an optical illusion. But how?! No one painted on the mustache, eyes, or hair. It’s just that from afar, vision does not perceive some small details, and puts more emphasis on large details.

The optical effect, which gives the viewer a false impression of the location of the seat, is due to the original design of the chair, invented by the French studio Ibride.

Peripheral vision turns beautiful faces into monsters.
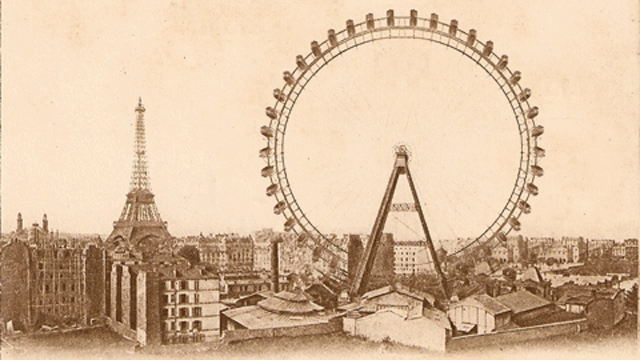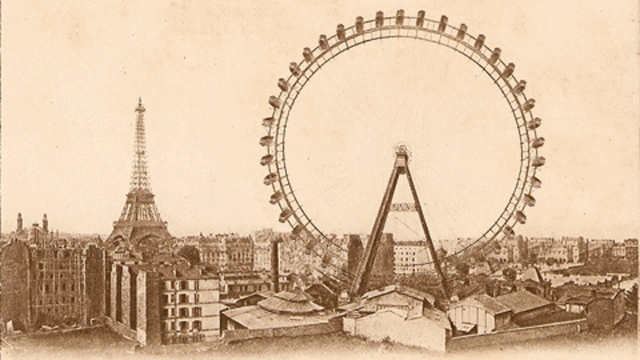
Which direction does the wheel spin?

Stare without blinking at the middle of the image for 20 seconds, and then move your gaze to someone’s face or just a wall.
ILLUSION OF WALL SIDE WITH WINDOW
On which side of the building is the window located? On the left, or maybe on the right?
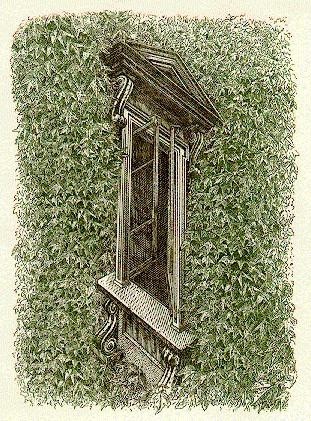
Once again our vision has been deceived. How did this become possible? It’s very simple: the upper part of the window is depicted as a window located on the right side of the building (we are looking, as if from below), and the lower part is on the left (we are looking from above). And the middle is perceived by vision as consciousness deems necessary. That's the whole deception.
Illusion of bars

Take a look at these bars. Depending on which end you are looking at, the two pieces of wood will either be next to each other, or one of them will be lying on top of the other.
Cube and two identical cups

Optical illusion created by Chris Westall. There is a cup on the table, next to which there is a cube with a small cup. However, upon closer examination, we can see that in fact the cube is drawn, and the cups are exactly the same size. A similar effect is noticeable only at a certain angle.
Illusion "Cafe Wall"

Take a close look at the image. At first glance, it seems that all the lines are curved, but in fact they are parallel. The illusion was discovered by R. Gregory at the Wall Cafe in Bristol. This is where its name came from.
Illusion of the Leaning Tower of Pisa

Above you see two pictures of the Leaning Tower of Pisa. At first glance, the tower on the right appears to lean more than the tower on the left, but in fact both of these pictures are the same. The reason is that the visual system views the two images as part of a single scene. Therefore, it seems to us that both photographs are not symmetrical.
ILLUSION OF WAVY LINES
There is no doubt that the lines depicted are wavy.

Remember what the section is called - optical illusion. You're right, these are straight, parallel lines. And it's a twisting illusion.
Ship or arch?

This illusion is a real work of art. The painting was painted by Rob Gonsalves, a Canadian artist, representative of the genre of magical realism. Depending on where you look, you can see either the arch of a long bridge or the sail of a ship.
ILLUSION - GRAFFITI “LADDER”
Now you can relax and not think that there will be another optical illusion. Let's admire the artist's imagination.

This graffiti was made by a miracle artist in the subway to the surprise of all passers-by.
BEZOLDI EFFECT
Look at the picture and say in which part the red lines are brighter and more contrasting. On the right isn't it?

In fact, the red lines in the picture are no different from each other. They are absolutely identical, again an optical illusion. This is the Bezoldi effect, when we perceive the tonality of a color differently depending on its proximity to other colors.
COLOR CHANGE ILLUSION
Does the color of the horizontal gray line change in the rectangle?

The horizontal line in the picture does not change throughout and remains the same gray. I can't believe it, right? This is an optical illusion. To make sure of this, cover the rectangle surrounding it with a sheet of paper.
THE ILLUSION OF A DECLINING SUN
This magnificent photograph of the sun was taken by the American space agency NASA. It shows two sunspots pointing directly at the Earth.

Something else is much more interesting. If you look around the edge of the Sun, you will see how it shrinks. This is truly GREAT - no cheating, a good illusion!
ZOLNER'S ILLUSION
Do you see that the herringbone lines in the picture are parallel?

I don't see it either. But they are parallel - check with a ruler. My vision was also deceived. This is the famous classic Zollner illusion, which has been around since the 19th century. Because of the “needles” on the lines, it seems to us that they are not parallel.
ILLUSION-JESUS CHRIST
Look at the picture for 30 seconds (it may take more), then move your gaze to a light, flat surface, such as a wall.

Before your eyes you saw the image of Jesus Christ, the image is similar to the famous Shroud of Turin. Why does this effect occur? In the human eye there are cells called cones and rods. Cones are responsible for transmitting a color image to the human brain under good illumination, and rods help a person see in the dark and are responsible for transmitting low-definition black-and-white images. When you look at a black and white image of Jesus, the sticks get tired due to long and intense work. When you look away from an image, these tired cells can't cope and can't transmit new information to the brain. Therefore, the image remains before the eyes and disappears when the sticks “come to their senses.”
ILLUSION. THREE SQUARE
Sit closer and look at the picture. Do you see that the sides of all three squares are curved?

I also see curved lines, despite the fact that the sides of all three squares are perfectly straight. When you move some distance away from the monitor, everything falls into place - the square looks perfect. This is due to the fact that the background causes our brain to perceive lines as curves. This is an optical illusion. When the background merges and we don’t see it clearly, the square appears even.
ILLUSION. BLACK FIGURES
What do you see in the picture?

This is a classic illusion. Taking a quick glance, we see some strange figures. But after looking a little longer we begin to distinguish the word LIFT. Our consciousness is accustomed to seeing black letters on a white background, and continues to perceive this word as well. It is very unexpected for our brain to read white letters on a black background. In addition, most people first look at the center of the picture, and this makes the task even more difficult for the brain, because it is used to reading a word from left to right.
ILLUSION. ILLUSION OF OUCHI
Look at the center of the picture and you will see a “dancing” ball.

This is an iconic optical illusion invented in 1973 by Japanese artist Ouchi and named after him. There are several illusions in this picture. First, the ball appears to move slightly from side to side. Our brain cannot understand that this is a flat image and perceives it as three-dimensional. Another deception of the Ouchi illusion is the impression that we are looking through a round keyhole at a wall. Finally, all the rectangles in the picture are the same size, and they are arranged strictly in rows without apparent displacement.
Optical illusions are created through simple manipulations of lines, colors and patterns to confuse our brains. Every day, optical illusions are increasingly used in art, entertainment, and audience-oriented scientific research. Since time immemorial, artists have come up with new ideas and techniques that require full sensory interaction with the viewers - something that would give their brains a big boost. Here is a list of 10 such optical illusion setups that will simply and literally confuse you.
18 PHOTOS
1. Invisible trolleybuses.  2. Casa Ceramica optical illusion.
2. Casa Ceramica optical illusion.  3. This illusion makes people afraid of falling over the moment they enter a room. This head-turning flooring system was designed by British company Casa Ceramica. Floors with this design have the specific purpose of slowing people down as they walk on it.
3. This illusion makes people afraid of falling over the moment they enter a room. This head-turning flooring system was designed by British company Casa Ceramica. Floors with this design have the specific purpose of slowing people down as they walk on it.  4. 3D zebra.
4. 3D zebra.  5. A zebra that will make you feel like you're floating in the air. It can be seen in the quaint fishing town of Isafjörður in Iceland. It was created in September this year as a result of collaboration between the city's environmental commissioner Ralkom Trulla and the street art firm Vegi GIH. They tried to reinforce both the aesthetic value of the city and remind motorists to slow down at crosswalks and on narrow streets.
5. A zebra that will make you feel like you're floating in the air. It can be seen in the quaint fishing town of Isafjörður in Iceland. It was created in September this year as a result of collaboration between the city's environmental commissioner Ralkom Trulla and the street art firm Vegi GIH. They tried to reinforce both the aesthetic value of the city and remind motorists to slow down at crosswalks and on narrow streets.  6. Large-scale geometric illusions of Felice Varini in Paris.
6. Large-scale geometric illusions of Felice Varini in Paris.  7. La Villette En Suites is an exhibition of the same name by Swiss artist Felice Varini opened in 2015. When viewing from one point, a strange feeling is created.
7. La Villette En Suites is an exhibition of the same name by Swiss artist Felice Varini opened in 2015. When viewing from one point, a strange feeling is created.  8. Varini, an architecture enthusiast, uses unconventional spaces with varying depths to create new geometric shapes that are basically paintings. These installations were available both inside and outside the Grande Halle de la Villette at the Parc de la Villette from April 15 to September 13, 2015.
8. Varini, an architecture enthusiast, uses unconventional spaces with varying depths to create new geometric shapes that are basically paintings. These installations were available both inside and outside the Grande Halle de la Villette at the Parc de la Villette from April 15 to September 13, 2015.  9. Retro city of optical illusions.
9. Retro city of optical illusions.  10. Photographed by Michael Paul Smith.
10. Photographed by Michael Paul Smith.  11. Green planet.
11. Green planet.  12. If you look at the composition from a certain angle and at a certain height, it will look like a globe with a few trees on top of it. In reality, however, it is a 1,500 square meter wide installation.
12. If you look at the composition from a certain angle and at a certain height, it will look like a globe with a few trees on top of it. In reality, however, it is a 1,500 square meter wide installation.  13. 3D gummy bears.
13. 3D gummy bears.  14. Optical illusions on buildings.
14. Optical illusions on buildings.  15. Mind-Bending Room settings.
15. Mind-Bending Room settings.  16. Want to experience how simple lines can make you tipsy? For you, there's Peter Kogler from Austria with his mind-blowing, psychedelic optical illusions. Kogler loves to bend time and space, which is what he does most interestingly. It transforms the flat floors and white walls of galleries into something strange. It uses completely two-dimensional, simple lines and bold graphics to fool perspective and change your own concepts of architecture.
16. Want to experience how simple lines can make you tipsy? For you, there's Peter Kogler from Austria with his mind-blowing, psychedelic optical illusions. Kogler loves to bend time and space, which is what he does most interestingly. It transforms the flat floors and white walls of galleries into something strange. It uses completely two-dimensional, simple lines and bold graphics to fool perspective and change your own concepts of architecture.  17. Interactive installation by Leandro Erlich.
17. Interactive installation by Leandro Erlich.  18. This is another art to completely get rid of your sense of coordination. Leandro Ehrlich, an artist from Argentina, gives an interactive experience to participants who get the illusion of sitting on the ledges of buildings. Known as Dalston House, it allowed people, young and old, to experience the thrill of performing the most daring stunts while remaining safe on the ground.
18. This is another art to completely get rid of your sense of coordination. Leandro Ehrlich, an artist from Argentina, gives an interactive experience to participants who get the illusion of sitting on the ledges of buildings. Known as Dalston House, it allowed people, young and old, to experience the thrill of performing the most daring stunts while remaining safe on the ground.
Optical illusion - pictures of illusions with explanations
Don't take optical illusions seriously, trying to understand and solve them, it's just how our vision works. This is how the human brain processes visible light from reflected images.
Unusual shapes and combinations of these pictures make it possible to achieve a deceptive perception, as a result of which it seems that the object is moving, changing color, or an additional picture appears.
All images are accompanied by explanations: how and how long you need to look at the picture to see something that is not really there.
For starters, one of the most discussed illusions on the Internet is 12 black dots. The trick is that you can't see them at the same time. A scientific explanation for this phenomenon was discovered by the German physiologist Ludimar Hermann in 1870. The human eye stops seeing the full picture due to lateral inhibition in the retina.


These figures move at the same speed, but our vision tells us otherwise. In the first gif, four figures move simultaneously while they are adjacent to each other. After separation, the illusion arises that they are moving along black and white stripes independently of each other. After the zebra disappears in the second picture, you can verify that the movement of the yellow and blue rectangles is synchronized.

Look carefully at the black dot in the center of the photo while the timer counts down 15 seconds, after which the black and white image will turn into color, that is, the grass is green, the sky is blue, and so on. But if you don’t stare at this point (to amuse yourself), the picture will remain black and white.

Without looking away, look at the cross and you will see a green spot running along the purple circles, and then they will completely disappear.

If you look at the green dot for a long time, the yellow dots will disappear.

Stare closely at the black dot and the gray stripe will suddenly turn blue.

If you cut a chocolate bar 5 by 5 and rearrange all the pieces in the order shown, an extra piece of chocolate will appear. Do this trick with a regular chocolate bar and it will never run out. (Joke).
From the same series.

Count the football players. Now wait 10 seconds. Oops! Parts of the picture are still the same, but one football player has disappeared somewhere!

The alternation of black and white squares within four circles creates the illusion of a spiral.

If you look in the middle of this animated picture, you will walk down the corridor faster, if you look to the right or left, you will walk slower.

On a white background, the gray stripe looks uniform, but as soon as the white background is replaced, the gray stripe immediately acquires many shades.

With a slight movement of the hand, the rotating square turns into chaotically moving lines.



The animation is obtained by overlaying a black grid on the drawing. Before our eyes, static objects begin to move. Even the cat reacts to this movement.

If you look at the cross in the center of the picture, your peripheral vision will turn the star faces of Hollywood actors into freaks.

Two pictures of the Leaning Tower of Pisa. At first glance, the tower on the right appears to lean more than the tower on the left, but in fact both of these pictures are the same. The reason is that the human visual system views two images as part of a single scene. Therefore, it seems to us that both photographs are not symmetrical.

Which direction does the subway train go?
This is how a simple color change can make the picture come to life.

We look for exactly 30 seconds without blinking, then we move our gaze to someone’s face, an object, or another picture.

A workout for the eyes... or for the brain. After rearranging the parts of the triangle, suddenly there is free space.
The answer is simple: in fact, the figure is not a triangle; the “hypotenuse” of the lower triangle is a broken line. This can be determined by the cells.

At first glance, it seems that all the lines are curved, but in fact they are parallel. The illusion was discovered by R. Gregory at the Wall Cafe in Bristol. That's why this paradox is called "The Wall in the Cafe."

Look at the middle of the picture for thirty seconds, then move your gaze to the ceiling or white wall and blink. Who did you see?

An optical effect that gives the viewer a false impression of how the chair is positioned. The illusion is due to the original design of the chair.

English NO (NO) turns into YES (YES) using curved letters.

Each of these circles rotates counterclockwise, but if you fix your gaze on one of them, the second circle will appear to rotate clockwise.

3D drawing on asphalt

Which direction does the Ferris wheel rotate? If you look to the left, then clockwise, if to the left, then counterclockwise. Perhaps it will be the other way around for you.

It's hard to believe, but the squares in the center are motionless.

Both cigarettes are actually the same size. Just place two cigarette rulers on the monitor, top and bottom. The lines will be parallel.

Similar illusion. Of course, these spheres are the same!

The droplets sway and “float”, although in reality they remain in their places, and only the columns in the background move.
Apparently reality depends on how the brain is able to interpret the environment. What if your brain receives false information through your senses, if your version of reality is not “real”?
The example images below are trying to trick your brain and show you a false reality. Have fun watching!
In fact, these squares are the same color. Place your finger horizontally on the border between both shapes and see how everything changes.

Photo: unknown
If you look at this lady's nose for 10 seconds and then blink quickly at a light surface, her face should appear in full color.

Photo: unknown
These cars look like they are different sizes...

Photo: Neatorama
But in reality they are the same.

These dots appear to change color and rotate around the center. But focus on one point - there is no rotation or color change.

Photo: reddit

Photo: unknown
This park in Paris looks like a giant 3D globe...

But in reality it is completely flat.

Photo: unknown
Which of the orange circles looks bigger?

Surprisingly, they are the same size.

Photo: unknown
Look at the yellow dot, then move closer to the screen - the pink rings will begin to rotate.

Photo: unknown
The Pinn-Brelstaff illusion occurs due to a lack of peripheral vision.
Believe it or not, the squares marked "A" and "B" are the same shade of gray.

Photo: DailyMail

Photo: WikiMedia
The brain automatically adjusts color based on surrounding shadows.
Look at this swirling picture for 30 seconds, and then move your attention to the photo below.


Photo: unknown
The previous GIF had tired your eyes, so the still photo came to life, trying to regain its balance.
“Ames Room” - the illusion creates confusion in the perception of the depth of the room by changing the angle of inclination of the back wall and ceiling.

Photo: unknown
The yellow and blue blocks seem to be moving one after the other, right?

Photo: Michaelbach
If you remove the black bars, you can see that the blocks are always parallel, but the black bars distort the perception of movement.
Move your head slowly towards the image and the light in the middle will become brighter. Move your head back and the light becomes weaker.

Photo: unknown
This is an illusion called "Dynamic Gradient Luminosity" by Alan Stubbs of the University of Maine.
Focus on the center of the color version, wait for the black and white to appear.

Photo: imgur
Instead of black and white, your brain fills the picture with the colors it thinks you should see based on orange and blue. Another moment - and you will return to black and white.
All the dots in this photo are white, but some appear black.

Photo: unknown
No matter how much you try, you will never be able to look directly at the blackheads that appear in the circles. How this illusion works has not yet been figured out.
By manipulating the human brain and vision, Brusspup is able to create amazing animations with just a black card.

Photo: brusspup
Dinosaur eyes are watching you...

Photo: brusspup
Akioshi Kitaoka uses geometric shapes, colors and vibrancy to create illusions of movement. These images are not animated, but the human brain sets them in motion.

Photo: ritsumel
Using similar techniques, Randolph creates similar, more psychedelic illusions.

Photo: flickr

Photo: Beau Deeley
Photographers can create amazing two-faced portraits by layering multiple images on top of each other.

Photo: Robble Khan
How does this train move? If you stare long enough, your brain will change direction.

Photo: unknown
Do you think the dancer in the middle is spinning clockwise or counterclockwise? Both ways.

Photo: unknown
The middle dancer changes direction depending on which girl you look at first: the one on the left or the one on the right.
Using clever design, artists like Ibride are able to create 3D art that looks incredible.

Photo: brusspup


Hold your gaze on the flashing green dot for a few seconds and you will see what happens to the yellow dots...

Photo: Michaelbach
Optical illusions are those effects of visual perception that occur involuntarily or consciously in a person observing certain images.
Such effects are also called optical illusions - errors in visual perception, the cause of which is the inaccuracy or inadequacy of the processes occurring during the unconscious correction of visual images. In addition, the physiological characteristics of the visual organs and the psychological aspects of visual perception also take part in the process of the occurrence of optical illusions.
Optical illusion, presented in this section of the site, consists of distorting perception by incorrectly assessing the length of segments, the size of angles, the colors of a visible object, etc. Its most popular types are illusions of depth perception, inversions, stereo pairs and illusions of movement.
Illusions of depth perception include inadequate reflection of the depicted object. The most famous examples of such illusions are two-dimensional contour pictures - when observing them, they are unconsciously perceived by the brain as single-convex. In addition, distortions in depth perception can lead to incorrect estimation of geometric dimensions (in some cases the error reaches 25%).
Optical illusion Inversion consists of depicting a picture, the perception of which depends on the direction of view.
Stereopairs allow you to observe a stereoscopic image by superimposing them on periodic structures. Focusing your gaze on the picture leads to the observation of a stereoscopic effect.
Moving illusions are periodic images, looking at them for a long time leads to the visual perception of movement from individual parts.
Do you see the frog and the horse in this optical illusion?
This picture is very famous. Turn it over to see how men see women after drinking 6 beers.
Mysterious face found on Mars. This is an actual photograph of the surface of Mars taken by Viking 1 in 1976.
Look at the four black dots in the center of the image for about 30-60 seconds. Then quickly close your eyes and turn towards something bright (a lamp or a window). You should see a white circle with an image inside.
Beautiful illusion of a moving bicycle (© Akiyoshi Kitaoka: used with permission).
Illusion of moving curtains (© Akiyoshi Kitaoka: used with permission).
Interesting optical illusion with perfect squares (© Akiyoshi Kitaoka: used with permission).
And once again perfect squares (© Akiyoshi Kitaoka: used with permission).
This is a classic - no need to explain.
There should be 11 faces in this picture. The average person sees 4-6, attentive people see 8-10. The best see all 11, schizophrenics and paranoids see 12 and more. What about you? (Don't take this test too seriously, I heard there might be 13 people there.)
Do you see a face in this pile of coffee beans? Don't rush, it's really there.
Do you see squares or rectangles? In reality, there are only straight lines in different directions, but our brain perceives them in a completely different way!









